| MAIN |
| ABOUT A PROJECT |
| OBJECTIVES |
| TEST REGIONS |
| DATA BASES |
| STUDY RESULTS |
| REPORTS |
| CONTACTS |
TASK 2: ASSISTANCE IN CREATING TWO WORLD FIRE WEB
The World Fire Web is a global system of forest fire monitoring. System development was first started in the Space Applications Institute (SAI) of the Joint Research Centre (JRC). The goal was to provide the scientists and experts, working in economy and politics, with up-to-date information with global coverage about area and locations of forest fires.
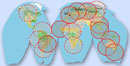
Structurally, this system is a fire net with global coverage. Nodes of the net are represented by ground receiving stations of NOAA satellites. Pic 1 illustrates the current development of the net and locations of the primary regional nodes of WFW. The automatic image processing performed at the nodes gives a possibility of real-time retrieval of daily regional forest fire maps, covering the node zone of responsibility. In the Receiving Centre of JRC, the global map is generated in real-time mode from the information retrieved from regional stations.
Within the project time frame, the International Forest Institute and IKI RAS participated in development of WFW net by providing assistance in fire node installation at the receiving stations, located in Russia. Here, we have accomplished the following tasks:
- A study of technical equipment and of the received data for a variety of receiving centers built on the territory of Russia. We tested the receiving centers of IKI RAS, ISTP SB RAS, and Sukachev Forest Institute SB RAS (Krasnoyarsk) as a potential candidate. The results of our research showed that all the centers have technical resources for fire node creation. After the quality analysis of the remote sensing information of the receiving stations it was decided to create the fire nodes at IKI RAS and at Sukachev Forest Institute SB RAS (Krasnoyarsk).
- The station formats were agreed upon. This permits to use the selected receiving stations in data processing systems of WFW nodes.
- We reached an agreement about the WFW node computer configuration. IKI RAS provided pre-installation of computers. Fire node software was installed by SAI experts on-line from the JRC data receiving and processing center.
- We reached a preliminary agreement about fire node installation with the Satellite Data Receiving Center of the Institute of Space Physics Researches and Aeronomy SB RAS (Yakutsk). We investigated the technical characteristics of this station and formats of data, received from AVHRR/NOAA satellites.
Currently, Moscow and Krasnoyarsk receiving stations are working in a test mode. The performance of software and hardware is being tested and corrected. The access to the nodes is provided by the JRC Data Receiving and Processing Center (http://wfw.gvm.sai.jrc.it) and directly from the servers of receiving stations in Moscow (http://wfw.iki.rssi.ru) and Krasnoyarsk (http:// wfw.academ.ru ).
TASK 3: PRE-FEASIBILITY STUDY FOR CONTINENTAL MAPPING OF RUSSIAN FORESTS USING COARSE RESOLUTION SATELLITE DATA (SPOT4-VEGETATION AND NOAA-AVHRR)
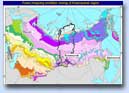
Because of a very large amount of satellite data necessary for full coverage of Russian territory and due to a very limited computing resource, we have decided within the pilot project to make a research on continental cartography in one of the test regions. This region has been chosen considering the extremely heterogeneous forest conditions, the existing of forestland categories and the types of forest. Taking into account these requirements, we have chosen Krasnoyarsk kray as a test region.Krasnoyarsk kray is situated in the Central Siberia and includes an exceptional amount of various forest vegetation zones of Siberia (Pic 2). The availability of up-to-date data of forest inventory for a large part of the region, medium and large-scale satellite imagery, and possibility to employ highly qualified specialists for the field works was the additional reason to settle on this region.
The total area of the forest fund of Krasnoyarsk kray is 137.2 millions ha as of 01.01.1993. The forested area of the forest fund of the region is 89.2 millions ha (65%). The main forest species of the region include pine, spruce, larch, cedar, fir, birch, and aspen.
TASK 4: DETECTION AND MAPPING OF ACTIVE FIRE DURING SUMMER 1998 OVER THE FAR EAST RUSSIAN REGION USING NOAA-AVHRR DATA
During the summer of 1998 the destructive wildfires occurred in the forests of Far East. These fires covered vast territories of Khabarovsk and Primorsky krays, Sakhalin island, Amurskaya oblast, and Sakha republic (Yakutia region). According to various information sources, the burned area totaled to 2 to 5 million ha. Table 5.1 encloses the official data of 1998 forest wildfires in entire Russia and in Far East alone. More than 90% of the total burned area belongs to the latter region. Similarly, more than 85% of 1998 crown wildfires in Russian forests were registered in Far East region.The 1998 wildfire information, according to Goscomstat (National committee on statistics) of Russia.
| Region | Burned area, ha | Damage enacted | ||||
| Forest lands | Non forest lands | Total | Crown fires alone | Million rubles | Thousand Euro | |
| Russia | 4268787,3 | 1070941,2 | 5339728,5 | 606693,8 | 6307,1 | ~ 458,7 |
| Far East | 3841901,7 | 989086,4 | 4830988,1 | 498102,0 | 5652,6 | ~ 410,1 |
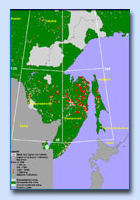
A vast area covered by forest fires in Far East was the motivation to conduct an experiment on wildfire detection and cartography using the archived NOAA-ANHRR 1998 data. To conduct the experiment, a 2,824,689 km2 test region was selected within Far East. This region belonged to the forested area under maximum fire damage (Pic 3), and had the following geographical coordinates: 50o -55o north latitude, 125o -145o east longitude.